Liptid: The Essential Role of Fatty Compounds in Health and Function
Liptid is a term that refers to a category of fatty compounds crucial for various physiological processes in the human body. These compounds play significant roles in maintaining cell structure, energy management, vitamin absorption, and hormone production. Understanding the importance of liptids can provide valuable insights into how our bodies function and how to optimize our health.
Introduction to Liptid
What is Liptid?
Liptid, derived from “lipid,” is a general term used to describe a diverse group of fatty compounds essential for numerous bodily functions. These compounds are integral to the structure and function of cells and are involved in a variety of biological processes. They are primarily categorized into several types, including phospholipids, glycolipids, and sphingolipids.
The Importance of Liptid in the Body
Liptids are fundamental to maintaining cell integrity and functionality. They form part of the cell membranes, where they help regulate the movement of substances into and out of cells. Additionally, liptids play crucial roles in energy storage, vitamin absorption, and hormone synthesis.
Types of Liptids and Their Functions
Phospholipids
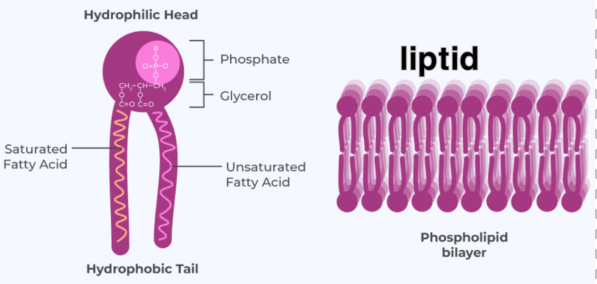
Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes. They consist of two fatty acid chains, a glycerol backbone, and a phosphate group. The amphipathic nature of phospholipids, with their hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and hydrophobic (water-repelling) tail, allows them to form bilayers that make up the cell membrane.
Key Functions of Phospholipids:
- Cell Membrane Structure: Phospholipids form the lipid bilayer that constitutes the cell membrane, providing structural support and creating a semi-permeable barrier.
- Signal Transduction: They are involved in signaling pathways that affect various cellular processes, including growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.
Glycolipids
Glycolipids are composed of a lipid moiety and one or more sugar molecules. They are found predominantly on the outer surface of cell membranes and play a role in cell-cell recognition and communication.
Key Functions of Glycolipids:
- Cell Recognition: Glycolipids contribute to cell-cell interactions and recognition, which are essential for tissue formation and immune responses.
- Protection: They help protect the cell surface from environmental damage and pathogens.
Sphingolipids
Sphingolipids are a diverse group of lipids that include sphingomyelins and glycosphingolipids. They are involved in maintaining the stability of cell membranes and modulating cellular signaling.
Key Functions of Sphingolipids:
- Myelin Sheath Formation: Sphingomyelins are essential for forming the myelin sheath around nerve cells, which facilitates efficient nerve impulse transmission.
- Cell Signaling: Sphingolipids are involved in various signaling pathways that regulate cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.
The Role of Liptid in Energy Management
Energy Storage
Liptids, particularly triglycerides, are a primary form of energy storage in the body. Triglycerides are composed of three fatty acid chains esterified to a glycerol molecule. They are stored in adipose tissue and released into the bloodstream when energy is needed.
Key Points:
- Fat Storage: Excess energy from food is converted into triglycerides and stored in fat cells for later use.
- Energy Release: When needed, triglycerides are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol, which are then used by the body for energy.
Metabolic Processes
Liptids are involved in various metabolic processes, including the synthesis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of the cell.
Key Points:
- Beta-Oxidation: Fatty acids are broken down in the mitochondria through beta-oxidation to produce ATP.
- Ketogenesis: In states of prolonged fasting or low carbohydrate intake, fatty acids are converted into ketone bodies, which serve as an alternative energy source.
Liptid and Vitamin Absorption
Role in Vitamin Absorption
Liptids are essential for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). These vitamins dissolve in fat and are absorbed along with dietary fats in the intestines.
Key Points:
- Vitamin Transport: Liptids help in the formation of micelles, which are critical for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
- Storage: Once absorbed, these vitamins are stored in the liver and adipose tissue, where they can be mobilized as needed.
Liptid and Hormone Production
Hormone Synthesis
Liptids play a crucial role in the synthesis of various hormones, including steroid hormones and eicosanoids.
Key Points:
- Steroid Hormones: Cholesterol, a type of liptid, is the precursor for steroid hormones such as cortisol, estrogen, and testosterone.
- Eicosanoids: These are signaling molecules derived from arachidonic acid, a type of fatty acid. They include prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxanes, which are involved in inflammation, immune responses, and blood clotting.
Health Implications of Liptid Imbalance
Liptid Deficiencies
Deficiencies in certain liptids can lead to various health issues, including:
- Cell Membrane Disorders: Inadequate phospholipid levels can affect cell membrane integrity and function, leading to issues such as neurological disorders and muscle weakness.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Insufficient dietary fats can impair the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, leading to deficiencies and related health problems.
Excess Liptids and Health Risks
Excessive accumulation of liptids, particularly in the form of triglycerides, can lead to health complications such as:
- Cardiovascular Disease: High levels of cholesterol and triglycerides are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Obesity: Excess fat storage can lead to obesity, which is a risk factor for various metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
Optimizing Liptid Health
Dietary Recommendations
To maintain healthy liptid levels and overall well-being, consider the following dietary recommendations:
- Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats in your diet, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. These foods provide essential fatty acids and support overall health.
- Limit Saturated Fats: Reduce intake of saturated fats found in processed foods and fatty meats, as they can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels.
- Balance Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids: Aim for a balanced intake of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids to support optimal health and reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle Factors
In addition to a balanced diet, adopting a healthy lifestyle can help optimize liptid levels:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to support healthy metabolism and manage body fat levels.
- Stress Management: Manage stress through relaxation techniques, as chronic stress can impact liptid metabolism and overall health.
FAQs About Liptid
1. What are liptids and why are they important?
- Liptids are fatty compounds essential for maintaining cell membrane structure, energy storage, vitamin absorption, and hormone production. They play a crucial role in various physiological functions and overall health.
2. What are the different types of liptids?
- The main types of liptids include phospholipids, glycolipids, and sphingolipids. Each type has specific functions, such as forming cell membranes, facilitating cell recognition, and aiding in nerve function.
3. How do liptids impact energy management in the body?
- Liptids, particularly triglycerides, store energy in adipose tissue and release it when needed. They are also involved in metabolic processes that produce ATP, the body’s primary energy source.
4. How do liptids affect vitamin absorption?
- Liptids are crucial for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). They form micelles in the intestines that help dissolve and transport these vitamins for absorption.
5. What are the health risks associated with imbalanced liptid levels?
- Imbalanced liptid levels can lead to health issues such as cardiovascular disease, obesity, and vitamin deficiencies. Maintaining healthy liptid levels is essential for overall well-being.
Conclusion
Liptids, a broad class of fatty compounds, are integral to numerous vital functions in the human body. From forming the essential structures of cell membranes to managing energy storage, aiding in vitamin absorption, and facilitating hormone production, liptids are fundamental to maintaining health and well-being.
By understanding the critical roles of liptids in the body, you can make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle to support optimal health. Whether it’s through balanced nutrition, regular exercise, or stress management, keeping liptid levels in check is key to maintaining a healthy and vibrant life.